Setup
Tools used for networking.
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade
sudo apt-get install netcat-openbsd tcpdump traceroute mtr
Theory
HTTP / TCP Model
Each of these depends on the one below. Some of these don't belong on a specific layer.
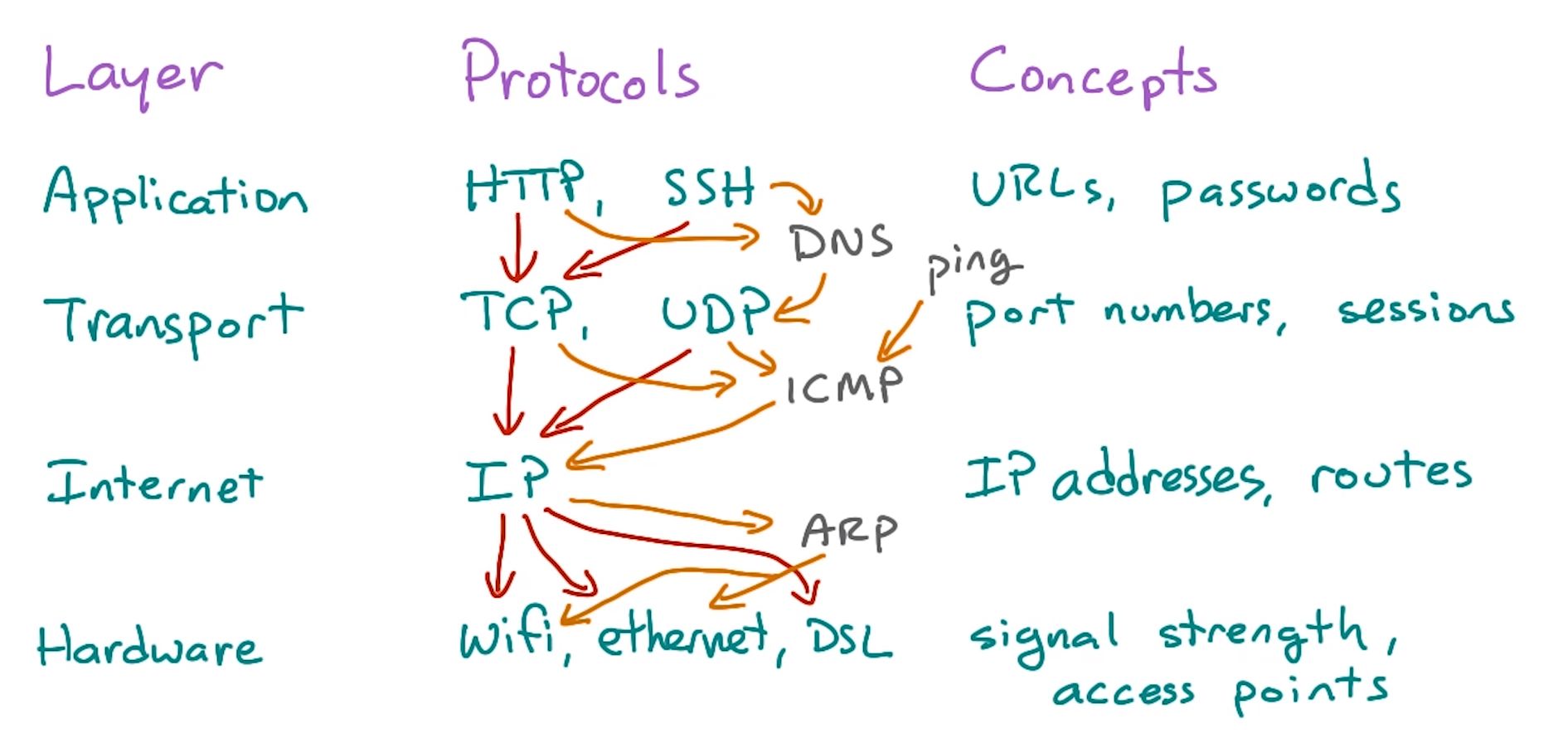
HTTP = Hypertext Transfer Protocol
TCP = Transmission Control Protocol
All traffic is split up into messages called packets, sent between two computers in a stream, with the addresses of the sender and recipient in each one.
HTTP is needed so that communicating systems can understand each other. TCP just provides "envelopes" that can transfer bytes around the network.
An application protocol assigns structure and meaning to the contents of the envelopes.
If you speak English and I send you a letter written in French, you'll still get the letter, but you won't understand it.
HTTP is implemented in browsers and web servers, while TCP in the operating system.
Simple HTTP Request
# HTTP header
GET /posts/1 HTTP/1.1
Host: jsonplaceholder.typicode.com
# Manual request - Returns header and body
printf 'GET /posts/1 HTTP/1.1\r\nHost:jsonplaceholder.typicode.com\r\n\r\n' | nc jsonplaceholder.typicode.com 80
# Just the body
curl jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1
Ports
Listening on a port is like waiting for a phone call on a specific phone number.
Ports let servers distinguish one service from another on the same host and wait for someone to connect.
Normally a server has well known ports for it's applications. ex. HTTP uses port 80 and SSH uses port 22. The client initiates a connection, and it's associated with an arbitrary port on its end.
Only one program can listen to a port in a given moment. Once started, the program can start child processe to listen for multiple connections on the same port i.e. a web server.
The port range that a normal (non-root) user can listen on is 1024 through 65535. Root access (including sudo)can listen on ports down to 1.
If the other side doesn't pick up, an RST (Reset packet) error message is sent back.
DNS
It's basically a phonebook for IP addresses.
An A Record is matched with an IP address, so when someone looks for www.google.com, the A record is referenced and the IP address is sent back to the user.
The DNS resolver i.e. client code is built into the OS.
CNAME - Canonical Name i.e. alias for a domain.
AAAA - IPv6 equivalent to an A record.
NS - DNS Name server. The NS record for a particular domain specifies which DNS has the records.
Tools
ping
It sends individual packets to test if traffic can get from one address to another, and back.
ping 8.8.8.8
# send 5 packets
ping -c 5 google.com
unknown host
sudo vim /etc/resolv.conf
# Add nameserver 8.8.8.8
lsof
The lsof utility lists open files, including network sockets (listening or connected).
# List only network sockets
lsof -i
nc / netcat
netcat is a tool for manually talking to servers, by connecting to a port and sending a string over it. It's a thing wrapper over TCP.
nc en.wikipedia.org 80
nc localhost 22
nc gmail-smtp-in.l.google.com 80
To illustrate, we can use two terminals to talk to each other. Anything typed at the second console will be concatenated to the first, and vice-versa. This is a simple TCP server. The connection is ended with CTRL + d.
# terminal 1
nc -l 3456 # listen for an incoming connection on port 3456
# typed text
# terminal 2
nc 127.0.0.1 3456 # connect to the machine and port being listened on
# typed text
Commands can be sent via a pipe.
echo 'message' | netcat server 80
netcat doesn't know anything about forming HTTP request, but in combination with printf and piping, it can be done.
printf 'HEAD / HTTP/1.1\r\nHost: google.com\r\n\r\n' | nc google.com 80
printf 'GET /posts/1 HTTP/1.1\r\nHost:jsonplaceholder.typicode.com\r\n\r\n' | nc jsonplaceholder.typicode.com 80
host
Used for looking up records in the DNS.
# Returns all the records
host google.com
# Returns just the A record
host -t a google.com
dig
Similar to host in showing DNS records, but in a way more readable for scripts and closer to the way they are stored in the DNS configuration files.
dig google.com
Static server
This will start a static web server on port 8000. The command has to be run in the directory with the index.html file.
python -m SimpleHTTPServer 8080
Networking
Gateway is the router address we are talking to in order to connect to the rest of the network/internet.
127.x.x.x - Your computer.
192.168.0.x - Local address created by a router.
ifconfig - Check IP address.
ping 8.8.8.8 - Ping IP address.
netstat -tupln - Check open ports.
cat etc/network/interfaces - Shows the interfaces brought up after booting.
/etc/hosts is used to simulate a domain for an IP address. Add 127.0.0.1 domain.com to avoid typing the IP address.